
Content Development
Levels of E-learning :
E-learning falls into four categories, from the very basic to the very advanced.
The categories are:
Knowledge databases -While not necessarily seen as actual training, these databases are the most basic form of E-learning. You have probably seen knowledge databases on software sites offering indexed explanations and guidance for software questions, along with step-by-step instructions for performing specific tasks. These are usually moderately interactive, meaning that you can either type in a key word or phrase to search the database, or make a selection from an alphabetical list.
Online support -Online support is also a form of E-learning and functions in a similar manner to knowledge databases. Online support comes in the form of forums, chat rooms, online bulletin boards, e-mail, or live instant-messaging support.Slightly more interactive than knowledge databases, online support offers the opportunity for more specific questions and answers, as well as more immediate answers.
Asynchronous training -This is E-learning in the more traditional sense of the word. It involves self-paced learning, either CD-ROM-based, Network-based, Intranet-based or Internet-based. It may include access to instructors through online bulletin boards, online discussion groups and e-mail. Or, it may be totally self-contained with links to reference materials in place of a live instructor.
Synchronous training - Synchronous training is done in real-time with a live instructor facilitating the training. Everyone logs in at a set time and can communicate directly with the instructor and with each other. You can raise your cyber hand and even view the cyber whiteboard. It lasts for a set amount of time -- from a single session to several weeks, months or even years. This type of training usually takes place via Internet web sites, audio- or video-conferencing, Internet telephony, or even two-way live broadcasts to students in a classroom.
E-learning Content Development:
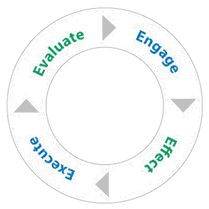
Engage
 Requirement Gathering: The client/end user requirements are gathered.
Requirement Gathering: The client/end user requirements are gathered. Learner Competency Mapping: The learner is profiled and the existing level of competency and motivation is gauged.
Learner Competency Mapping: The learner is profiled and the existing level of competency and motivation is gauged. Skill Gap Analysis: The gap between the learning requirements and the learner competency is analyzed.
Skill Gap Analysis: The gap between the learning requirements and the learner competency is analyzed. Learning Goals and Learning Outcome: The expected learner behaviour on completion of the learning and the steps to achieve the goals are listed. The parameters for measurement of the effectiveness of the content are decided.
Learning Goals and Learning Outcome: The expected learner behaviour on completion of the learning and the steps to achieve the goals are listed. The parameters for measurement of the effectiveness of the content are decided.
 Delivery Mode: The E-learning standards to be adhered to (for instance, SCORM, AICC, and QTI) and the deployment mode upon completion (online or blended) are also decided at this stage.
Delivery Mode: The E-learning standards to be adhered to (for instance, SCORM, AICC, and QTI) and the deployment mode upon completion (online or blended) are also decided at this stage.
Effect
 Instructional Design and Treatment: An overall strategy to provide effective learning to the audience −motivational aspects is developed.
Instructional Design and Treatment: An overall strategy to provide effective learning to the audience −motivational aspects is developed. Learning Matrix: Learning objects are designed to include concept presentation, handholding, interactivity, and assessments.
Learning Matrix: Learning objects are designed to include concept presentation, handholding, interactivity, and assessments. Content and Storyboarding Guidelines: Style guides and other guidelines for the various multimedia elements are laid down.
Content and Storyboarding Guidelines: Style guides and other guidelines for the various multimedia elements are laid down. User Interface and Template Design: The functional features of the content along with the layout and look and feel are designed.
User Interface and Template Design: The functional features of the content along with the layout and look and feel are designed. Graphics and Programming Design: Graphics Design parameters, programming flowcharts, and modules are designed.
Graphics and Programming Design: Graphics Design parameters, programming flowcharts, and modules are designed. Standards Design: The standards that were decided upon are designed for execution.
Standards Design: The standards that were decided upon are designed for execution.
Execute
 Scripting and Storyboarding: A visual storyboard and a textual script to guide the production is developed.
Scripting and Storyboarding: A visual storyboard and a textual script to guide the production is developed. Construction of Media Elements: Text, graphics, audio, video, and animations are individually constructed or repurposed to suit the required learning objects.
Construction of Media Elements: Text, graphics, audio, video, and animations are individually constructed or repurposed to suit the required learning objects.
 Interaction Programming: The appropriate logic for the learning object is then implemented through multiple constructs at various levels.
Interaction Programming: The appropriate logic for the learning object is then implemented through multiple constructs at various levels. Integration and Packaging as per Standards: The content objects are then aggregated, integrated, and packaged as per pre-defined standards.
Integration and Packaging as per Standards: The content objects are then aggregated, integrated, and packaged as per pre-defined standards.
Evaluate
 Staged Review: At every phase, testing and review is done against the requirements matrix to close the gaps.
Staged Review: At every phase, testing and review is done against the requirements matrix to close the gaps. Goals and Objectives Evaluation: Goals and objectives are checked against the developed artifacts.
Goals and Objectives Evaluation: Goals and objectives are checked against the developed artifacts. Impact Measurement and Benefit Analysis: At the pilot stage and post implementation, the benefits accrued to the learners are checked against the originally desired impact.
Impact Measurement and Benefit Analysis: At the pilot stage and post implementation, the benefits accrued to the learners are checked against the originally desired impact.
